What Does Not Change When A Solution Is Diluted By The Addition Of Solvent
iv.5: Solution Concentration and Dilution
The relative amount of a given solution component is known as its concentration. Ofttimes, though not e'er, a solution contains ane component with a concentration that is significantly greater than that of all other components. This component is called the solvent and may be viewed as the medium in which the other components are dispersed or dissolved. Solutions in which h2o is the solvent are, of course, very mutual on our planet. A solution in which water is the solvent is called an aqueous solution.
A solute is a component of a solution that is typically present at a much lower concentration than the solvent. Solute concentrations are often described with qualitative terms such equally dilute (of relatively low concentration) and concentrated (of relatively high concentration).
Concentrations may be quantitatively assessed using a wide variety of measurement units, each convenient for item applications. Molarity (M) is a useful concentration unit for many applications in chemistry. Molarity is divers as the number of moles of solute in exactly 1 liter (i 50) of the solution and has the units of 'mol/L'.
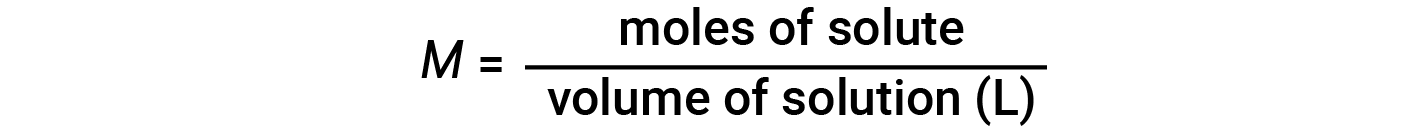
Note that in the molarity equation, the book of solution, and not the volume of solvent, is used. This is because, depending on the nature of interactions between the solute and solvent, the solute tin change the volume of the solution. Hence, in the molarity equation, nosotros employ the full solution volume (i.e., solvent book + solute volume). Considering solution volumes vary with temperature, molar concentrations will likewise vary. When expressed as molarity, the concentration of a solution with identical numbers of solute and solvent species volition be unlike at unlike temperatures, due to the contraction/expansion of the solution.
Dilution of Solutions
Dilution is the process whereby a solution is made less full-bodied (or more dilute) by the addition of solvent. For instance, a glass of iced java becomes increasingly dilute, and less sweet, as the ice melts. In laboratories, solutions are ofttimes stored in their concentrated forms, called stock solutions. Solutions of lower concentrations are prepared from stock through dilution.
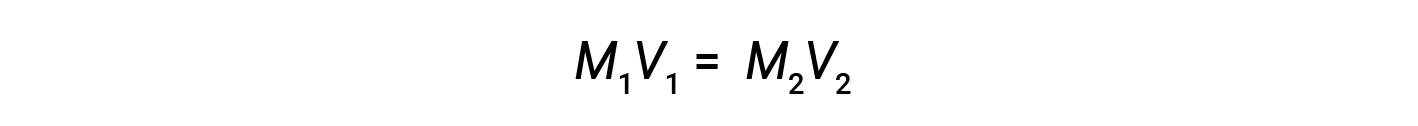
where M and V are concentration and book, respectively, and the subscripts "1" and "2" refer to the solution before and later on the dilution, respectively.
At present, since the product of molarity and book equals moles, the number of moles earlier and after dilution stays the same.
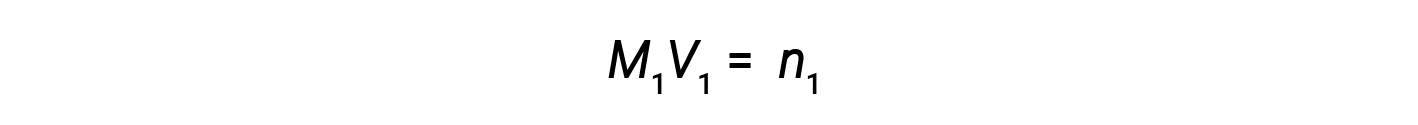
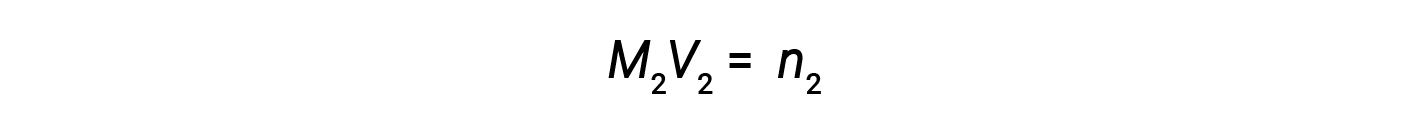
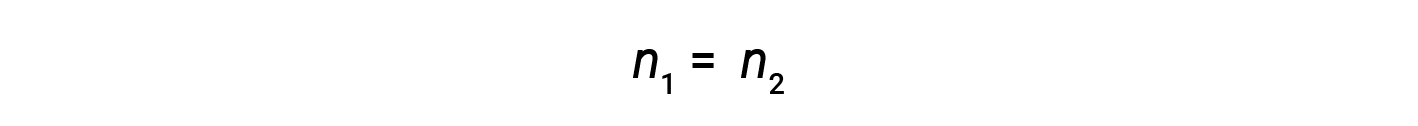
Thus, dilution does not change the amount of solute in the solution.
This text is adapted from OpenStax Chemistry 2e, Section 3.three: Molarity.
Source: https://www.jove.com/science-education/11263/solution-concentration-and-dilution
Posted by: harristuddly.blogspot.com


0 Response to "What Does Not Change When A Solution Is Diluted By The Addition Of Solvent"
Post a Comment